CIB image toolbox technical manual
| Site: | CIB eLearning |
| Course: | CIB image toolbox |
| Book: | CIB image toolbox technical manual |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Tuesday, 10 March 2026, 8:27 AM |
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Calling CIB image toolbox
- 3. Input CIB IPL properties
- 4. Output CIB IPL properties
- 5. Properties details
- 5.1. InputFilename
- 5.2. AlgorithmSetFileName
- 5.3. AlgorithmSetData
- 5.4. OutputDirectory
- 5.5. OutputFileNamePatterns
- 5.6. TraceFilename
- 5.7. PageSelection
- 5.8. Overwrite
- 5.9. Threading
- 5.10. ErrorBehavior
- 5.11. OriginPageCount
- 5.12. OriginMimeType
- 5.13. OriginImagePageInfo
- 5.14. ResultFileNamePatterns
- 5.15. ResultCount
- 5.16. ProcessingStatus
- 6. Image processing algorithms: Filters
- 7. Image information
- 8. Mergers
- 9. Segmenters
- 10. Image comparer
- 11. Algorithms sets
- 12. CIB aiModule
- 13. Returncodes
1. Introduction
This library contains implementations of a number of image processing algorithms for scanned documents processing.
These algorithms can be separated into next categories:
- Filters:
- Noise filters
- Binarization filters
- Modification filters
- Affine transform filters
- Special filters
- Image information
- Mergers
- Segmenters
- Image comparers
2. Calling CIB image toolbox
Calling via CIB job: example CIB job XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?>
<!-- XML jobfile für CIB job from version 1.0.4 --><root>
<!-- Definition of Jobs or Steps that a sent to documentserver from the caller --> <Comod> <!-- Default settings that are valid for all Jobs and Commands, if they are not overwritten in the job or step -->
<defaults><properties command="job"> <property name="OutputMode">XML</property> <property name="UseInMemoryProcessing">1</property> </properties>
</defaults>
<!-- List of all jobs in this job --> <jobs><job name="job1" expected-result-code="0"><!-- List of all steps that are to be executed in this Job --><steps><step name="ipl"command="image-conversion"> <properties> <property name="InputFilename">c:/Test/1/test.tif</property>
<property name="OutputDirectory">c:/Test/1/</property> <property name="OutputFileNamePatterns">pattern_png_###;pattern_jpeg_prev_##; pattern_jpeg_thumbs_##</property> <property name="PageSelection">{ "PageRange" : "1", "Encoding" : "PNG", };{"PageRange" : "2", "Encoding" :
"JPEG", };{ "PageRange" : "1-10", "Encoding" :"JPEG", "MaxWidth" : "150" }</property> <property name="Overwrite">true</property> <property name="Threading">{ "SelectionThreads": "3", "RenderThreads" : "3" }</property>
</properties> </step>
</steps> </job>
</jobs> </Comod>
</root>
Calling via CIB runshell
cibrsh -d request.xml
3. Input CIB IPL properties
|
Name |
Possible values |
Default |
Data type |
|
InputFilename |
Path to a file |
|
String |
|
OutputDirectory |
Path to a directory |
|
String |
|
OutputFileNamePatterns |
“pattern[;pattern]” |
|
String |
|
TraceFilename |
Any filename |
|
String |
|
PageSelection |
{“PageRange”:”<start>[-<end>]”, |
|
JSON |
|
Overwrite |
“True”, “False” |
False |
Boolean |
|
Threading |
“SelectionThreads”: number, |
SelectionThreads: 1, RenderThreads: 1 |
String |
|
ErrorBehavior |
“Stop”, “Continue”, “Fill” |
Continue |
String |
|
OperationName |
For instance |
|
String |
4. Output CIB IPL properties
|
Name |
Possible values |
Default |
Data type |
|
OriginPageCount |
<number> |
|
Number |
|
OriginMimeType |
<IANA MimeType> |
|
String |
|
OriginImagePageInfo |
{“PageRange”:”<start[-<end>]", |
|
JSON |
|
ResultFileNamePatterns |
“pattern[;pattern]” |
|
String |
|
ResultCount |
“count per pagerange[;count per pagrange]” |
|
String |
|
ProcessingStatus |
{”Status”:OK|NOK,
|
|
JSON |
5. Properties details
In this chapter you can find details about different properties.
5.1. InputFilename
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
InputFilename |
String |
Set |
Specifies the filename of the input file. Supported image formats: BMP, PNG, JPEG, TIFF, SVG.
Syntax
InputFilename=filename.<ext>
<ext>: Supported image formats
Example
InputFilename=file.tif5.2. AlgorithmSetFileName
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
AlgorithmsSetFileName
|
String
|
Set
|
Specifies the filename of the XML defining algorithms.
Syntax
AlgorithmsSetFileName=algorithms.xml
Example
AlgorithmsSetFileName=algorithms.xml
5.3. AlgorithmSetData
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
AlgorithmsSetData
|
String
|
Set
|
Specifies the raw XML string data to be processed. This property overrides contents found on AlgorithmsSetFileName.
Syntax
AlgorithmsSetData=<XML>
Example
AlgorithmsSetData=
<algorithms> <algorithm name="CleanImage" inputs="InputFile=$1" outputs="CleanedImage=$0"> <processor type="CleanBackgroundToWhiteFilter" inputs="InputFile" outputs="CleanedImage" /> </algorithm>
</algorithms>
5.4. OutputDirectory
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
OutputDirectory
|
String |
Set
|
Specifies the output directory. ‘Absolute’ and ‘relative’ specifications are allowed. The File name is specified by the property OutputFileNamePatterns.
Syntax
OutputDirectory=.\Folder\
Example
OutputDirectory=.\Folder\5.5. OutputFileNamePatterns
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
OutputFileNamePatterns |
String |
Set |
With this property a pattern for output filenames can be specified.
Per pageselection there is one pattern. If no pattern is preset, a unique name is generated that also contains a number pattern for multipage files. Placeholder for numbers is the hashtag “#”, where if there are several # Symbols, zeros are filled from the left. That means: “###” leads to “000” - “099”, but the value is not limited to the number of digits as represented by # Symbols. So the value for a placeholder “###” could be “123456789”.
This value can optionally contain a relative directory (e.g. “output\manipulatedImage”). However the directory must be ‘relative’ specified.
Syntax
OutputFileNamePatterns=<pattern>[;<pattern>]
<pattern>:<Patternname>_###.<ext>
<ext>: Supported image formats
Example
OutputFileNamePatterns=pattern_png_###.tif5.6. TraceFilename
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
TraceFilename |
String |
Set |
Specifies the name of the log file (and, optionally, directory). If this property is set, a log file of the process is created. However the directory may only be defined ‘relative’.
Syntax
TraceFilename=filename.log
Example
TraceFilename=output\trace.log5.7. PageSelection
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
PageSelection |
String |
Set |
Property for page selection. With this property you can describe, which page/pages should be processed.
If this property is not set or no parameters are passed, there is no conversion process and the logfile contains ‘Conversion isn't required: PageSelection isn't defined.’
Must only be positive values, otherwise conversion
will fail with error.
‘Conversion
parameter array is invalid or empty.’
Syntax
PageSelection={“PageRange”:”<start>[-<end>]”,”MaxWidth”: number, ” MaxHeight”: number, “MaxResolutionX”: number, “MaxResolutionY”: number, “ColorSpace”: string, “ColorDepth”: number, “Encoding”: string, [[“CompressionLevel”:number][, “Quality”:number] [, “Border”: { “Width”: number, “Color”: string}][, “SpecialPageRange”: {“PageRange”:”<start>[-<end>]”, ”MaxWidth”: number, ”MaxHeight”: number, …}][, “ImageToolboxParams”: { “AlgorithmSetPath”: string, “AlgorithmName”: string, “ProfilePath”: string]}] [, “…”:…]]};...
Example
Example #1:
PageSelection={ "PageRange" :"1", "Encoding" : "PNG", };{"PageRange" : "2", "Encoding" : "JPEG",};{ "PageRange" : "1-10", "Encoding" : "JPEG",
"MaxWidth" : "150" }
Example #2:
{ "PageRange" :"1-3", "Encoding" : "TIFF","ColorSpace" : "sRGB", "ColorDepth" :"8", "MultiPageOutput" : true,
"ImageToolboxParams" : { "AlgorithmSetPath" :"c:/Software/CIB/_IPL_problems/2016_11_29/AlgorithmsSet_sample.xml","AlgorithmName" : "Flip", "ProfilePath" :
"c:/Software/CIB/_IPL_problems/2016_11_29/processing_profile.xml", },"Border" : { "Width" : "3", "Color" :"0,255,0", }, "SpecialPageRange" : { "PageRange"
: "2-2", "AutoRotation":false, "MaxHeight" :"1000", "Border" : { "Width" : "5","Color" : "255,0,0", }, "ImageToolboxParams" : {"AlgorithmSetPath" :
"c:/Software/CIB/_IPL_problems/2016_11_29/AlgorithmsSet_sample.xml","AlgorithmName" : "Invert", "ProfilePath1" :
"c:/Software/CIB/_IPL_problems/2016_11_29/processing_profile.xml", },}, }
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
Possible values |
Default |
|
PageRange |
<start> [-<end>] |
Page range |
Accepts only positive numbers |
|
|
MaxWidth |
Number |
Maximum width of an input image |
Accepts only positive numbers |
0 |
|
MaxHeight |
Number |
Maximum height of an input image |
Accepts only positive numbers |
0 |
|
MaxResolutionX |
Number |
Maximum X resolution of an image |
Accepts only positive numbers |
0 |
|
MaxResolutionY |
Number |
Maximum Y resolution of an image |
Accepts only positive numbers |
0 |
|
ColorSpace |
String |
Output color space of an image |
See here |
sRGB |
|
ColorDepth |
Number |
Output color depth of an image |
Accepts only positive numbers |
0 |
|
Encoding |
String |
Output encoding of an image |
Any supported by IPL image format |
JPEG |
|
CompressionLevel |
Number |
Quality for PNG format. See more in Quality property |
Numbers in the range [0; 100]. 100 is the highest quality |
50 |
|
Compression |
Number |
Same as CompressionLevel. CompressionLevel has higher priority |
Numbers in the range [0; 100]. 100 is the highest quality |
50 |
|
Quality |
Number |
Regulates quality of an output image. See more here |
Numbers in the range [0; 100]. 100 is the highest quality |
-1 |
|
Border |
JSON |
Specializes border for an image |
|
|
|
SpecialPageRange |
ImageToolboxParams |
Contains specials params for some PageRange It may contain the same properties like the parent PageRange does. The Default Values however are not set for the SpecialPageRange |
Any valid JSON with right properties |
|
|
AutoRotation |
Boolean |
Enable autorotation based on EXIF information |
True | False |
True |
|
KeepAspectRatio |
Boolean |
Keep ratio between sides |
True | False |
False |
|
MultiPageOutput |
Boolean |
Regulates multi page output |
True | False |
False |
|
ExpandImage |
Boolean |
Fit image in an output image size. If False, crops an image |
True | False |
True |
|
Width |
Number/String |
Set output image width |
Any positive number |
|
|
Width_Top |
Number/String |
Set border width at top |
Any positive number |
|
|
Width_Bottom |
Number/String |
Set border width at bottom |
Any positive number |
|
|
Width_Left |
Number/String |
Set border width at left |
Any positive number |
|
|
Width_Right |
Number/String |
Set border width at right |
Any positive number |
|
|
Color |
Number/String |
Set color for border |
Set of three colors [0; 255] |
|
|
Color_Top |
Number/String |
Set color for border at top |
Set of three colors [0; 255] |
|
|
Color_Bottom |
Number/String |
Set color for border at bottom |
Set of three colors [0; 255] |
|
|
Color_Left |
Number/String |
Set color for border at left |
Set of three colors [0; 255] |
|
|
Color_Right |
Number/String |
Set color for border at right |
Set of three colors [0; 255] |
|
5.8. Overwrite
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
Overwrite |
Boolean |
Set |
Specifies, must or not the library overwrite output images.
Syntax
Overwrite=<bool>
<bool>: true | false
Example
Overwrite=false5.9. Threading
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
Threading |
String |
Set |
This property allows to control how many parallel threads should be used.
Syntax
Threading=”SelectionThreads:<number>, RenderThreads: <number>”
Example
Threading=”SelectionThreads: 3,RenderThreads: 3”5.10. ErrorBehavior
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
ErrorBehavior |
String |
Set |
This property controls what should happen in case of an error.
Syntax
ErrorBehavior=<behavior>
<behavior>: Stop| Continue | Fill
Stop:
In the case of a failed conversion, the procedure stops with a runtime error and the message “Error behaviour defined as ‘Stop’. Convertion was stopped.
Continue: (Default)
Fill:
Force creation of blob or image although convertion failed.
Example
ErrorBehavior=Continue5.11. OriginPageCount
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
OriginPageCount |
Number |
Get |
This property always refers to the source file and returns number of pages.
Syntax
OriginPageCount=<number>
Example
OriginPageCount=25.12. OriginMimeType
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
OriginMimeType |
String |
Get |
Returns the MimeType of the source file.
Syntax
OriginMimeType=<IANA MimeType>
Example
OriginMimeType=image/tiff5.13. OriginImagePageInfo
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
OriginImagePageInfo |
JSON |
Get |
Returns detailed meta information about the source files. For example resolution and size, color space and color depth, encoding and the according page selection.
Syntax
OriginImagePageInfo=
<ext>: tif|etc |
Example
OriginImagePageInfo={"ColorDepth": 1, "ColorSpace": "Gray","Encoding": "Group4", "Height": 2327, "PageRange":"1-1", "ResolutionX": 200, "ResolutionY": 200, "Width": 1647 } ;{ "ColorDepth": 8, "ColorSpace":"Gray", "Encoding": "JPEG", "Height":2348, "PageRange": "2-2", "ResolutionX": 200,"ResolutionY": 200, "Width": 1674 }
5.14. ResultFileNamePatterns
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
ResultFileNamePatterns |
String |
Get |
Information about the used patterns for filenames.
Syntax
ResultFileNamePatterns=<pattern>[;<pattern>]
<pattern>:<patternname>_###.<ext>
<ext>: png | jpg | tif |…
Example
ResultFileNamePatterns=”pattern_png_%03d.png;pattern_jpeg_prev_%02d.jpg; pattern_jpeg_thumbs_%02d.jpg”5.15. ResultCount
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
ResultCount |
JSON |
GET |
This JSON object describes the amount of pages that have been processed.
Syntax
ResultCount=<count per pagerange>[;<count per pagerange>]
Example
ResultCount{
"Count": 10,
"IsResultMultipage":false,
"PageRange": "1-10"
}
5.16. ProcessingStatus
|
Property-Name |
Data type |
Type |
|
ProcessingStatus |
JSON |
Get |
Provides information about the state of processing, which operation was or is conducted, in what area and if the operation was successful.
Syntax
ProcessingStatus=Operation:<operation>, PageRange: <pagerange>, RequiredRange:<requiredrange>, Status: <status>
<operation>: Convertion | |
<pagerange>: <number> | <number>-<number>
<requiredrange>: <number> | <number>-<number>
<sstatus>: OK | NOK
Example
ProcessingStatus={Operation":"Convertion", "PageRange": "0","RequiredRange": "0", "Status": "OK" };{ "Operation": "Convertion", "PageRange":
"1", "RequiredRange": "1", "Status":"OK" } ;{ "Operation": "Convertion","PageRange": "0-1", "RequiredRange": "2","Status": "OK" }
Although the input for PageRange in the jobinterface starts with number 1 (e.g. “1-4”, the PageRange of the ProcessingStatus starts with (e.g. “0-3”).
Image Processing Library usage
Filters
For using filters you should perform next steps:
1. Include header for filters:
#include "ImageProcessing_Filtration.h"
2. Create default utilities sets and copy them to new ProcessingProfile:
UtilitiesSets sets = UtilitiesSetsCreator::CreateUtilitiesSets();
ProcessingProfile profile;
profile.m_Utilities = sets.utilities;
profile.m_DebugUtilities = sets.debugUtilities;
3. Create profile parser and parse selected profile:
shared_ptr<ProfileParser> profileParser(ProfileParserCreator::CreateProfileParser());
profileParser->ParseProfile(profileFileName, profile);
4. Load image for processing:
RasterImage imageToProcess;
shared_ptr< IPL::IOStreams::ImageDecoder > imageDecoder(
IPL::IOStreams::ImageDecodersFabric::CreateImageDecoder());
IPL::IOStreams::InputStream inputStream(inputFileName);
imageToProcess = imageDecoder->decode(inputStream);
5. Create default filter creator (fabric):
shared_ptr<ImageFilterCreator> filterCreator(
ImageFilterCreatorsSelector::SelectImageFilterCreator() );
6. Create filters:
int binarizationFilterType = IFK_SAVOULA_BINARIZER;
int noiseFilterType =IFK_HUANG_BILATERAL_FILTER;
shared_ptr<ImageFilter> binarizationFilter(
filterCreator->CreateFilter(binarizationFilterType, profile) );
shared_ptr<ImageFilter> noiseFilter(
filterCreator->CreateFilter(noiseFilterType, profile) );
7. Process image:
RasterImage processedImage;
processedImage = binarizationFilter->apply(noiseFilter->apply(imageToProcess));
8. Show processing result:
profile.m_DebugUtilities->ShowImage("Window Title for Processed Image", processedImage);
9. And store it:
shared_ptr< IPL::IOStreams::ImageEncoder > encoder( IPL::IOStreams::ImageEncodersFabric::CreateImageEncoder(IPL::IOStreams::IEK_JPG_ENCODER));
IPL::IOStreams::OutputStream outputStream(inputFileName + ".proc" + ".jpg");
encoder->encode(processedImage, outputStream);
Look for sample FiltrationSample() in ImageProcessing_sample.cpp.
Segmenters
For using segmenters you should perform next steps:
1. Include header for segmenters:
#include "ImageProcessing_Segmentation.h"
2. Create default utilities sets and copy them to new ProcessingProfile:
UtilitiesSets sets = UtilitiesSetsCreator::CreateUtilitiesSets();
ProcessingProfile profile;
profile.m_Utilities = sets.utilities;
profile.m_DebugUtilities = sets.debugUtilities;
3. Create profile parser and parse selected profile:
shared_ptr<ProfileParser> profileParser(ProfileParserCreator::CreateProfileParser());
profileParser->ParseProfile(profileFileName, profile);
4. Load image for processing and create array for results:
RasterImage imageToProcess;
RasterImageArray results;
profile.m_DebugUtilities->ReadImageFromFile(inputFileName, imageToProcess);
5. Create default segmenter creator (fabric)
shared_ptr<ImageSegmenterCreator> segmenter_creator(
ImageSegmenterCreatorsSelector::SelectImageSegmenterCreator() );
6. Create segmenter:
int segmenterType = ISK_RANGES_SEGMENTER;
shared_ptr<ImageSegmenter> segmenter(
segmenter_creator->CreateSegmenter(segmenterType, profile));
7. Process image:
segmenter->segment(imageToProcess, results);
8. Save processing result to files:
for (size_t imageNo = 0; imageNo < results.size(); ++imageNo) {
profile.m_DebugUtilities->WriteImageToFile(results[imageNo],
inputFileName + ".layer_" + std::to_string(imageNo) + ".jpg");
}
or
shared_ptr<IPL::IOStreams::ImageEncoder> encoder(
IPL::IOStreams::ImageEncodersFabric::CreateImageEncoder(IPL::IOStreams::IEK_JPG_ENCODER));
for (size_t imageNo = 0; imageNo < results.size(); ++imageNo) { IPL::IOStreams::OutputStream outoutStream(
inputFileName + ".layer_" + std::to_string(imageNo) + ".jpg"); encoder->encode(results[imageNo], outoutStream);
}
Look for sample SegmentationSample() in ImageProcessing_sample.cpp.
User defined filters[edit | edit source]
For developing new filter (or segmenter) you should perform next steps:
1. Include header for filters:
#include "ImageProcessing_Filtration.h"
2. Create new class which inherits class ImageFilter (or ImageSegmenter for segmenters).
3. Create implementations of methods for new class:
virtual bool Initialize(ProcessingProfile& profile);
virtual RasterImage::RasterImagePtr apply(RasterImage& image) final;
For using of new filter (or segmenter) you should perform next steps:
1. Create default filter creator (fabric):
shared_ptr<ImageFilterCreator> filterCreator(
ImageFilterCreatorsSelector::SelectImageFilterCreator() );
2. Create lambda for new filter creation:
ImageFilterCreator::ImageFilterCreationProcedure newFilterCreationProcedure =
[](ProcessingProfile& profile) -> ImageFilter*
{
return new UserDefinedImageFilter(profile);
};
3. Add new filter to fabric:
uint32_t newFilterKey = filterCreator->AddFilter(newFilterCreationProcedure);
4. Create profile and set processing parameters
ProcessingProfile profile;
profile["UserDefinedImageFilter/Parameter1"] = "1";
5. Create instance of user defined filter
shared_ptr<ImageFilter> userDefinedFilter(
filterCreator->CreateFilter(newFilterKey, profile) );
6. Process image by filters
processedImage = userDefinedFilter->apply(noiseFilter->apply(imageToProcess)); Look for sample class UserDefinedImageFilter and UserDefinedImageFilter_sample() in ImageProcessing_sample.cpp.
Usage of DLL interface
CIB Job interface
Functions of this interface described in IPL_Interface.h.
Interface for doXisafe
For usage of the library from doXisafe ScenarioExecuter is available. It can be used by calling function CibImageProcessingRunScenario() declared in IPL_ScenarioExecuter_Interface.h.
Improvement functionality using plugins
IPL functionality can be improved by external module which are separated dynamically loading libraries.
Plugin interface
For developing IPL plugin you should implement functions declared in file IPL_Plugin_Interface.h as .dll (for Windows) or .so (for Linux):
PluginInterfaceVersionType GetPluginInterfaceVersion();
bool InitializePlugin(const std::string& pluginParametersString);
RasterImage* RunPlugin(RasterImage& inputImage);
bool DestroyPlugin();
Also library IPL_Plugin_Base.lib should be linked to your plugin.
Plugin usage
For using of plugin special filter was implemented. Key of this filter is IPL::Filtration::IFK_PLUGIN_FILTER.
Plugin file and corresponding processing parameters should be defined in processing profile
<ExternalFilter>
<PluginFileName>IPL_Plugin_sample.dll</PluginFileName>
<PluginParametersString>1</PluginParametersString>
</ExternalFilter>
or manually by correction of properties map
profile["PluginFileName/PluginParametersString"] = "0";
Processing profiles
Processing profiles are used for describing of processing parameters for implemented filters. Profile is a file in XML format with next structure (order of descriptions and filters/segmenters parameters does not matter):
<ProcessingProfile> <Filter1> <Filter1_Parameter1>Filter1_Parameter1_Value</Filter1_Parameter1> ... <Filter1_ParameterN>Filter1_ParameterN_Value</Filter1_ParameterN> </Filter1> ... <FilterM> <FilterM_Parameter1>FilterM_Parameter1_Value</FilterM_Parameter1> ... <FilterM_ParameterK>FilterM_ParameterK_Value</FilterM_ParameterK> </FilterM> <Merger1> <Merger1_Parameter1>Merger1_Parameter1_Value</Merger1_Parameter1> ... <Merger1_ParameterY>Merger1_ParameterY_Value</Merger1_ParameterY> </Merger1> ... <MergerL> <MergerL_Parameter1>MergerL_Parameter1_Value</MergerL_Parameter1> ... <MergerL_ParameterX>MergerL_ParameterX_Value</MergerL_ParameterX> </MergerM> <Segmenter1> <Segmenter1_Parameter1>Segmenter1_Parameter1_Value</Segmenter1_Parameter1> ... <Segmenter1_ParameterY>Segmenter1_ParameterY_Value</Segmenter1_ParameterY> </Segmenter1> ... <SegmenterL> <SegmenterL_Parameter1>SegmenterL_Parameter1_Value</SegmenterL_Parameter1> ... <SegmenterL_ParameterX>SegmenterL_ParameterX_Value</SegmenterL_ParameterX> </SegmenterM> </ProcessingProfile>
6. Image processing algorithms: Filters
Filters are divided into: Affine transform filters, Binarization
filters, Modification filters, Noise Filters, Special filters.
6.1. Affine transform filters
CroppingFilterDocumentCropper
DocumentDeskewer
FlippingFilter
ResizeFilter
RotationFilter
DocumentCleaner
RotateAndMirrorFilter
CroppingFilter
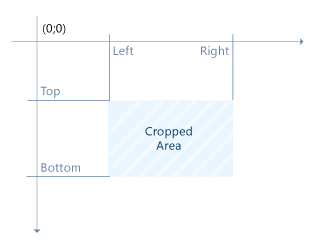
This filter allows cropping of defined area of original image. Area for cropping can be defined in two ways:
- By separated borders,
- By single line.
In both cases you should keep in mind coordinate system of image. Pixel with coordinates (0;0) is located in top left corner of image:
For example definitions
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<CroppingFilter> <IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired>1</IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired> <CroppingArea>100;500;100;500</CroppingArea> </CroppingFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
<ProcessingProfile>
... <CroppingFilter> <IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired>1</IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired> <Top>100</Top> <Bottom>500</Bottom> <Left>100</Left> <Right>500</Right> </CroppingFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
are equal.
Also filter can be used for cropping quadrangular areas. In this case user should define area as set of four clockwise points in format x0;y0;x1;y1;x2;y2;x3;y3:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <CroppingFilter> <IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired>1</IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired>
<CroppingArea>100;100;500;250;500;500;150;500</CroppingArea>
</CroppingFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
In addition with usage of flag IsResizingToSourceSizeRequired (if it is not equal 0) result of cropping can be resized to size of original image.
Also you can define background color:
<BackgroundColor>0;0;0</BackgroundColor>
DocumentCropper
The filter auto-crops an input image.
This algorithm has no parameters.
Example
<step command="ipl"expected-result-code="0" name="ImageProcessingStep_page_1” timeout="0"> <properties> <property name="WorkSpace">.\</property> <property name="OperationName">DocumentCropper</property> <property name="OutputFileName">cropedImage.png</property> <property name="OutputDirectory">.\</property> <property name="InputFilename">inputs\Versatel.png</property> <property name="TraceFilename">file.log</property> </properties> </step>
DocumentDeskewer
The filter deskews an input image.
Parameters:
|
Property Name |
Description |
Default value |
|
Profile:DocumentDeskewer/DetectOrientation |
Detects image orientation and rotates it to the correct position (possible degrees of rotation only multiple of 90). |
1 |
<step command="ipl" expected-result-code="0" name="ImageProcessingStep_page_1” timeout="0">
<properties>
<property name="WorkSpace">.\</property>
<property name="OperationName">DocumentDeskewer</property>
<property name="OutputFileName">deskewedImage.png</property>
<property name="OutputDirectory">.\</property>
<property name="InputFilename">inputs\Versatel.png</property>
<property name="TraceFilename">file.log</property>
</properties>
</step>
Flips an input image.
Parameters:
|
Property Name |
Description |
Default value |
|
FlippingDirectionCode |
Code of flipping operation direction:
|
1 |
ResizeFilter
Image resizing filter.
Parameters of image resizing can be set in two ways:
By scaling. In this case we should set parameter "ResizeFilter/ResizingParameter" to required scale value:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ResizeFilter> <ResizingParameter>0.5</ResizingParameter>
</ResizeFilter>
...
\endcod
</ProcessingProfile>e
-# By defining of target size. In this case we should set parameter
"ResizeFilter/ResizingParameter"
to required size value:
\code{.xml}
<ProcessingProfile>
... <ResizeFilter> <ResizingParameter>W;H</ResizingParameter> </ResizeFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
where W is target width, H – height. If W or H is equal to 0 then this value will be calculated depends on other size and source image geometry. For example:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <ResizeFilter>
<ResizingParameter>0;1000</ResizingParameter>
</ResizeFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
In this case width will be calculated:
height = 1000;
width = sourceImage.Width * (height / sourceImage.Height);
If W or H is less than 0 or empty then corresponding size will not be changed. For example samples
<ProcessingProfile>
... <ResizeFilter> <ResizingParameter>-1;1000</ResizingParameter> </ResizeFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
and
<ProcessingProfile>
... <ResizeFilter> <ResizingParameter>;1000</ResizingParameter>
</ResizeFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
are equal and create image with width <sourceImage.Width>x1000 pixels.
RotationFilter
Interface for image clockwise rotation filter.
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
RotationAngle |
Rotation angle (in degrees) |
0.0 |
DocumentCleaner
The DocumentCleaner gets an input image and tries to eliminate fog and uneven light so that the output looks almost like a scan.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <DocumentCleaner> <BrightSpots>0</BrightSpots>
</DocumentCleaner>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
BrightSpots |
Enable this if the input image contains bright spots, for better performance of the algorithm. |
false |
RotateAndMirrorFilter
Filter for rotation and image mirroring.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <RotateAndMirrorFilter> <Degrees>0</Degrees> <Mirror>false</Mirror>
</RotateAndMirrorFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
Degrees |
Degrees of rotation to be applied, only multiple of 90. |
0 |
|
Mirror |
If enabled, image will be mirrored. |
false |
6.2. Binarization filters
The following chapters explain each filter. Usually there is also an example given. The input image for the filters is the following picture:
FBCITB_Binarizer
FengBinarizerFilter
GaussianBlurFilter
LocalOtsuBinarizer
MedianBlurAGTFilter
MedianBlurATFilter
MedianBlurGATFilter
NativeAdaptiveBinarizer
NiblackBinarizerFilter
NICKBinarizerFilter
OtsuBinarizer
PureAdaptiveGaussianThresholdingFilter
PureAdaptiveThresholdingFilter
SauvolaBinarizerFilter
ThresholdFilter
WolfJolionBinarizerFilter
COCOCLUST_Binarizer
Parameters: Threshold:45|CLAHEClipLimit:3.0|GaussianBlurKernelSize:19|CannyUpperThresholdCoeff:0.15 |
Output: |
Implementation of COCOCLUST binarization.
This binarizator is described in the publication Kasar, T. and Ramakrishnan, A.G., 2009. COCOCLUST: Contour-based color clustering for robust binarization of colored text. Proc. The Third CBDAR, pp.11-17.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <COCOCLUST_Binarizer> <Threshold>45</Threshold> <CLAHEClipLimit>3.0</CLAHEClipLimit> <GaussianBlurKernelSize>19</GaussianBlurKernelSize> <CannyUpperThresholdCoeff>0.15</CannyUpperThresholdCoeff> <CannyLowerThresholdCoeff>0.05</CannyLowerThresholdCoeff> <CannyMorphIters>4</CannyMorphIters> </COCOCLUST_Binarizer>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
Property name | Description | Default value |
Threshold | Threshold for preliminary clustering procedure | 45 |
CLAHEClipLimit | Parameter for CLAHE procedure | 3.0 |
GaussianBlurKernelSize | Parameter for Gaussian blur procedure | 19 |
CannyUpperThresholdCoeff | Coefficient for upper threshold of Canny edge detector | 0.15 |
CannyLowerThresholdCoeff | Coefficient for lower threshold of Canny edge detector | 0.05 |
CannyMorphIters | Parameter of morphology operations | 4 |
FBCITB_Binarizer
|
Parameters: UseCanny:1|UseVariancesMap:1 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of FBCITB binarization.
This binarizator is described in Kasar, T., Kumar, J. and Ramakrishnan, A.G., 2007, September. Font and background color independent text binarization. In Second international workshop on camera-based document analysis and recognition (pp. 3-9).
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <FBCITB_Binarizer> <UseCanny>1</UseCanny> <UseVariancesMap>0</UseVariancesMap> <VarianceMapThreshold>200</VarianceMapThreshold> <CLAHEClipLimit>2.0</CLAHEClipLimit> <GaussianBlurKernelSize>9</GaussianBlurKernelSize> <CannyUpperThresholdCoeff>0.6</CannyUpperThresholdCoeff> <CannyLowerThresholdCoeff>0.4</CannyLowerThresholdCoeff> <BoundingRectangleMaxArea>0.3</BoundingRectangleMaxArea> </FBCITB_Binarizer>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
UseCanny |
Is not equal 0 if Canny border detection is required |
1 |
|
UseVariancesMap |
Is not equal 0 variances map is used for contour detection |
0 |
|
VarianceMapThreshold |
Variance threshold |
200 |
|
CLAHEClipLimit |
Parameter for CLAHE procedure |
2.0 |
|
GaussianBlurKernelSize |
Parameter for Gaussian blur procedure |
9 |
|
CannyUpperThresholdCoeff |
Coefficient for upper threshold of Canny edge detector |
0.6 |
|
CannyLowerThresholdCoeff |
Coefficient for lower threshold of Canny edge detector |
0.4 |
|
BoundingRectangleMaxArea |
Coefficient for the bounding rectangle area |
0.3 |
|
Parameters: WindowSize:21|Alpha1:0.7|k1:0.2|k2:0.03|Gamma:2.0|MorphIterationCount:2 |
|
Output: |

Implementation of Feng binarization.
This binarizator is described in Khurshid, K., Siddiqi, I., Faure, C. and Vincent, N., 2009, January. Comparison of Niblack inspired binarization methods for ancient documents. In Document Recognition and Retrieval XVI (Vol. 7247, p. 72470U). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <FengBinarizerFilter> <WindowSize>21</WindowSize>
<Alpha1>0.7</Alpha1>
<k1>0.2</k1>
<k2>0.03</k2>
<Gamma>2.0</Gamma>
<MorphIterationCount>2</MorphIterationCount> </FengBinarizerFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
WindowSize |
Size of sliding window |
21 |
|
Alpha1 |
Coefficient for threshold calculation |
0.7 |
|
k1 |
Coefficient for threshold calculation |
0.2 |
|
k2 |
Coefficient for threshold calculation |
0.03 |
|
Gamma |
Coefficient for threshold calculation |
2.0 |
|
MorphIterationCount |
Count of iterations of final dilate and erode operations |
2 |
GaussianBlurFilter
In image processing, a Gaussian blur is the result of blurring an image by a Gaussian function. This function used to reduce Image noise and detail.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
Please note that “KernelSize” only accept odd numbers!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<algorithms>
<algorithm name="ImageManipulation" TracingEnabled="false" inputs="in1=$1" outputs="out4=$1">
<layer>
<processor params="KernelSize:21" type="GaussianBlurFilter" outputs="out4" inputs="in1" />
</layer>
</algorithm>
</algorithms>
LocalOtsuBinarizer
|
Parameters: CLAHEClipLimit:0.0|GaussianBlurKernelSize:19|CannyUpperThresholdCoeff:0.15|CannyLowerThresholdCoeff:0.01|MaxValue:255.0|CannyMorphIters:1 |
|
Output: |

Implementation of Otsu binarization algorithm.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<LocalOtsuBinarizer> <MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue> <CLAHEClipLimit>0.0</CLAHEClipLimit> <GaussianBlurKernelSize>19</GaussianBlurKernelSize> <CannyUpperThresholdCoeff>0.15</CannyUpperThresholdCoeff> <CannyLowerThresholdCoeff>0.01</CannyLowerThresholdCoeff> <CannyMorphIters>1</CannyMorphIters> </LocalOtsuBinarizer>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
MaxValue |
Maximal value |
255.0 |
|
CLAHEClipLimit |
Parameter for CLAHE procedure |
0.0 |
|
GaussianBlurKernelSize |
Parameter for Gaussian blur procedure |
19 |
|
CannyUpperThresholdCoeff |
Coefficient for upper threshold of Canny edge detector |
0.15 |
|
CannyLowerThresholdCoeff |
Coefficient for lower threshold of Canny edge detector |
0.01 |
|
CannyMorphIters |
Parameter of morphology operations |
1 |
MedianBlurAGTFilter
|
Parameters: KernelSize:3|BlockSize:5|Shift:0.0|MaxValue:255.0 |
|
Output: |

Median blur + Adaptive Gaussian threshold filter.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<MedianBlurAGTFilter> <KernelSize>3</KernelSize> <MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue> <BlockSize>5</BlockSize> <Shift>0.0</Shift>
</MedianBlurAGTFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
KernelSize |
Size of kernel of median blur filter |
3 |
|
BlockSize |
Size of sliding window |
5 |
|
Shift |
Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean |
0.0 |
|
MaxValue |
Color of background of binarized image |
255.0 |
MedianBlurATFilter
|
Parameters: KernelSize:3|BlockSize:5|Shift:0.0|MaxValue:255.0 |
|
Output: |

Median blur + Adaptive threshold filter.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<MedianBlurATFilter> <KernelSize>3</KernelSize> <MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue> <BlockSize>5</BlockSize> <Shift>0.0</Shift>
</MedianBlurATFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
KernelSize |
Size of kernel of median blur filter |
3 |
|
BlockSize |
Size of sliding window |
5 |
|
Shift |
Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean |
0.0 |
|
MaxValue |
Color of background of binarized image |
255.0 |
MedianBlurGATFilter
|
Parameters: Default Parameters |
|
Output: |

Gaussian blur + Adaptive threshold filter.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<MedianBlurGATFilter>
<KernelSize>3</KernelSize>
<SigmaX>10.0</SigmaX>
<SigmaY>0.0</SigmaY> <MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue> <BlockSize>5</BlockSize> <Shift>0.0</Shift>
</MedianBlurGATFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
KernelSize |
Size of kernel of median blur filter |
3 |
|
SigmaX |
Sigma for horizontal direction |
10.0 |
|
SigmaY |
Sigma for vertical direction |
0.0 |
|
MaxValue |
Color of background of binarized image |
255.0 |
|
BlockSize |
Size of sliding window |
5 |
|
Shift |
Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean |
0.0 |
|
Parameters: Default Parameters |
|
Output: |
Native adaptive thresholding.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<NativeAdaptiveBinarizer> <IsGaussianBlurReqiured>0</IsGaussianBlurReqiured> <MedianBlurKernelSize>5</MedianBlurKernelSize> <GaussianBlurKernelSize>3</GaussianBlurKernelSize>
<GaussianBlurSigma>150</GaussianBlurSigma <IsAdaptiveThresholdCalculatedByGaussian>1</IsAdaptiveThresholdCalculatedByGaussian> <AdaptiveThresholdingMaxValue>255.0</AdaptiveThresholdingMaxValue> <AdaptiveThresholdingBlockSize>19</AdaptiveThresholdingBlockSize> <AdaptiveThresholdingShift>8</AdaptiveThresholdingShift> <BilateralFilterBlockSize>5</BilateralFilterBlockSize> <BilateralFilterColorSigma>50.0</BilateralFilterColorSigma> <BilateralFilterSpaceSigma>50.0</BilateralFilterSpaceSigma>
</NativeAdaptiveBinarizer>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
IsGaussianBlurReqiured |
Flag of usage Gaussian blur |
0 |
|
MedianBlurKernelSize |
Kernel size for median blur |
5 |
|
GaussianBlurKernelSize |
Kernel size for Gaussian blur |
3 |
|
GaussianBlurSigma |
Gaussian blur sigma |
150 |
|
IsAdaptiveThresholdCalculatedByGaussian |
Flag of base of adaptive thresholding type |
1 |
|
AdaptiveThresholdingMaxValue |
New value for pixel which intensity greater than threshold value |
255.0 |
|
AdaptiveThresholdingBlockSize |
Kernel size for adaptive thresholding procedure |
19 |
|
AdaptiveThresholdingShift |
Shifting value for adaptive thresholding procedure |
8 |
|
BilateralFilterBlockSize |
Kernel size for bilateral filtration. If less than 0 then filtration isn't used |
5 |
|
BilateralFilterColorSigma |
Sigma for intensity range |
50.0 |
|
BilateralFilterSpaceSigma |
Sigma for space range |
50.0 |
NiblackBinarizerFilter
|
Parameters: WindowSize:101|ThresholdCoefficient:0.01|MorphIterationCount:2 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of Niblack binarization.
This binarizator is described in Khurshid, K., Siddiqi, I., Faure, C. and Vincent, N., 2009, January. Comparison of Niblack inspired binarization methods for ancient documents. In Document Recognition and Retrieval XVI (Vol. 7247, p. 72470U). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<NiblackBinarizerFilter> <WindowSize>101</WindowSize> <ThresholdCoefficient>0.01</ThresholdCoefficient> <MorphIterationCount>2</MorphIterationCount> </NiblackBinarizerFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
WindowSize |
Size of sliding window |
101 |
|
ThresholdCoefficient |
Coefficient $k$ for threshold calculation |
0.01 |
|
MorphIterationCount |
Count of iterations of final dilate and erode operations |
2 |
NICKBinarizerFilter
|
Parameters: WindowSize:101|ThresholdCoefficient:0.01|MorphIterationCount:2 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of NICK binarization.
This binarizator is described in Khurshid, K., Siddiqi, I., Faure, C. and Vincent, N., 2009, January. Comparison of Niblack inspired binarization methods for ancient documents. In Document Recognition and Retrieval XVI (Vol. 7247, p. 72470U). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <NICKBinarizerFilter> <WindowSize>101</WindowSize> <ThresholdCoefficient>0.01</ThresholdCoefficient> <MorphIterationCount>2</MorphIterationCount> </NICKBinarizerFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
WindowSize |
Size of sliding window |
101 |
|
ThresholdCoefficient |
Coefficient $k$ for threshold calculation |
0.01 |
|
MorphIterationCount |
Count of iterations of final dilate and erode operations |
2 |
OtsuBinarizer
|
Parameters: MaxValue:255 |
|
Output: |
Interface for Otsu binarization algorithm.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<OtsuBinarizer> <MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue>
</OtsuBinarizer>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
MaxValue |
Color of background of binarized image |
255.0 |
PureAdaptiveGaussianThresholdingFilter
|
Parameters: MaxValue:255|BlockSize:5|Shift:0.0 |
|
Output: |

Pure adaptive Gaussian thresholding filter.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>...
<PureAdaptiveGaussianThresholdingFilter>
<MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue>
<BlockSize>5</BlockSize>
<Shift>0.0</Shift>
</PureAdaptiveGaussianThresholdingFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
MaxValue |
Color of background of binarized image |
255.0 |
|
BlockSize |
Size of sliding window |
5 |
|
Shift |
Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean |
0.0 |
PureAdaptiveThresholdingFilter
|
Parameters: MaxValue:255|BlockSize:5|Shift:0.0 |
|
Output: |

Pure adaptive thresholding filter.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<PureAdaptiveThresholdingFilter> <MaxValue>255.0</MaxValue> <BlockSize>5</BlockSize> <Shift>0.0</Shift>
</PureAdaptiveThresholdingFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
MaxValue |
Color of background of binarized image |
255.0 |
|
BlockSize |
Size of sliding window |
5 |
|
Shift |
Constant subtracted from the mean or weighted mean |
0.0 |
SauvolaBinarizerFilter
|
Parameters: WindowSize:101|ThresholdCoefficient:0.00|MorphIterationCount:2 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of Sauvola binarization.
This binarizator is described in Shafait, F., Keysers, D. and Breuel, T.M., 2008, January. Efficient implementation of local adaptive thresholding techniques using integral images. In Document recognition and retrieval XV (Vol. 6815, p. 681510). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <SauvolaBinarizerFilter> <WindowSize>101</WindowSize> <ThresholdCoefficient>0.01</ThresholdCoefficient> <MorphIterationCount>2</MorphIterationCount> </SauvolaBinarizerFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
WindowSize |
Size of sliding window |
101 |
|
ThresholdCoefficient |
Coefficient for threshold calculation |
0.01 |
|
MorphIterationCount |
Count of iterations of final dilate and erode operations |
2 |
|
Parameters: ThresholdValues:100;128;90 |
|
Output: |
Pure thresholding binarizator.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ThresholdFilter>
<ThresholdValues>100;128;90</ThresholdValues>
</ThresholdFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
ThresholdValues |
Values of threshold for each color channel |
100; 128; 90 |
Also we can define equal value of thresholds for each channel:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ThresholdFilter>
<ThresholdValues>128</ThresholdValues>
</ThresholdFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
WolfJolionBinarizerFilter
|
Parameters: WindowSize:101|ThresholdCoefficient:0.00|MorphIterationCount:2 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of WolfJolion binarization.
This binarizator is described in Khurshid, K., Siddiqi, I., Faure, C. and Vincent, N., 2009, January. Comparison of Niblack inspired binarization methods for ancient documents. In Document Recognition and Retrieval XVI (Vol. 7247, p. 72470U). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<WolfJolionBinarizerFilter> <WindowSize>101</WindowSize> <ThresholdCoefficient>0.01</ThresholdCoefficient> <MorphIterationCount>2</MorphIterationCount> </WolfJolionBinarizerFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
WindowSize |
Size of sliding window |
101 |
|
ThresholdCoefficient |
Coefficient for threshold calculation |
0.01 |
|
MorphIterationCount |
Count of iterations of final dilate and erode operations |
2 |
6.3. Modification filters
AlphaMaskFilterAutoInvertFilter
CleanBackgroundToWhiteFilter
CloseFilter
ColorRangesFilter
ColorSpaceConvertionFilter
ContrastEnhancementFilter
DilateFilter
ErodeFilter
GuoHallThinningFilter
HistogramEqualizationFilter
InvertFilter
OpenFilter
ZhangSuenThinningFilter
ColorRangeConverter
BalanceWhiteFilter
ColorBalanceFilter
ColorSwapFilter
AlphaMaskFilter
Filter for alpha channel thresholding.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<AlphaMaskFilter> <Threshold>128</Threshold> <IsInvertedMaskRequired>0</IsInvertedMaskRequired> <IsBinaryMaskRequired>1</IsBinaryMaskRequired>
</AlphaMaskFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
Threshold |
Threshold value for applying |
128 |
|
IsInvertedMaskRequired |
If it is not equal 0 then obtained mask should be inverted |
0 |
|
IsBinaryMaskRequired |
– If it is not equal 0 then obtained mask should be binary image else – halftone |
1 |
AutoInvertFilter
|
Parameters: |
|
Output: |
Implementation of auto inversion procedure.
Image will be inverted if a number of non-black point is greater or equal than half of image area.
This filter have no parameters.
CleanBackgroundToWhiteFilter
|
Parameters: gamma:1.0|blackValue:70|whiteValue:170 |
|
Output: |
The filter cleans background with making all near-white colors true white color.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<CleanBackgroundToWhiteFilter> <gamma>1.0</gamma> <blackValue>70</blackValue> <whiteValue>170</whiteValue>
</CleanBackgroundToWhiteFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
gamma |
Gamma value |
1.0 |
|
blackValue |
Set black value threshold for the algorithm |
70 |
|
whiteValue |
Set white value threshold for the algorithm binary image else – halftone |
170 |
CloseFilter
|
Parameters: IterationCount:2 |
|
Output: |
Morphology operation 'Close'.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<CloseFilter> <IterationCount>1</IterationCount>
</CloseFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
IterationCount |
Number of iteration of procedure |
1 |
ColorRangesFilter
|
Parameters: <default Parameters> |
|
Output: |
Interface for color ranges filter.
This filter allows to extract from image all pixels with colors that fall within user defined ranges (or if it is required pixel that do not fall within these ranges). These ranges can be defined by definition of lower and upper range boundary:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ColorRangesFilter> <IsMaskOnlyRequired>0</IsMaskOnlyRequired>
<IsInRangeColorsRequired>0</IsInRangeColorsRequired> <LowerBoundaries>0,0,0;130,55,80</LowerBoundaries> <UpperBoundaries>128,128,128;209,190,190</UpperBoundaries> <RangeShapes>b(0, 0, 0, 127, 127, 127)</RangeShapes> </ColorRangesFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
Color ranges can be defined in two ways:
- by color values boundaries (LowerBoundaries and UpperBoundaries options)
- by definition of shapes in colorspace (RangeShapes option; this option has higher priority).
For color values boundaries usage we should define lower and upper values of color for each color range:
<LowerBoundaries>R1_L,G1_L,B1_L;R2_L,G2_L,B2_L</LowerBoundaries>
<UpperBoundaries>R1_U,G1_U,B1_U;R2_U,G2_U,B2_U</UpperBoundaries>
where R1_L – lower boundary of red color for the first range, R1_U – upper boundary of red color for the first range.
The same results can be obtained using the second way: we can define corresponding boxes (rectangular shapes):
<RangeShapes>b(R1_L,G1_L,B1_L, R1_U,G1_U,B1_U);b(R2_L,G2_L,B2_L, R2_U,G2_U,B2_U)</RangeShapes>
Also spherical shapes can be used:
<RangeShapes>s(centerR, centerG, centerB, diameter)</RangeShapes>
There is special way for spherical shapes usage: we can use set of spheres to definition of extensional areas. For example, if we have following spheres set:
<RangeShapes>s{(5, 5, 5, 30) - (50, 50, 50, 40) - (100, 100, 50, 50) - (100, 100, 200, 25) - (200, 100, 50, 25)}</RangeShapes>
then we will obtain next 3D area for color selection (intermediate spheres parameters would be calculated automatically).
If IsMaskOnlyRequired is not equal 0 then we
obtain only binary mask for defined color ranges.
ColorSpaceConvertionFilter
|
Parameters: TargetColorspace:HSV|SourceColorspace:RGB |
|
Output: |
Interface of image color space convertion procedure.
This filter can be used for transforming current color space of image (this information can be obtained from input image) to user defined color space.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ColorSpaceConvertionFilter> <TargetColorspace>HSV</TargetColorspace> <SourceColorspace>RGB</SourceColorspace>
</ColorSpaceConvertionFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
TargetColorspace |
required color space |
|
|
SourceColorspace |
color space of source image |
|
Currently implemented next conversions are:
- RGB -> GRAY
- RGB -> BGR
- RGB -> HSV
- RGB -> HLS
- RGB -> Lab
- RGB -> Luv
- RGB -> XYZ
- RGB -> YUV
- RGB -> YCrCb
- GRAY -> RGB
- BGR -> RGB
- HSV -> RGB
- HLS -> RGB
- Lab -> RGB
- Luv -> RGB
- XYZ -> RGB
- YUV -> RGB
- YCrCb -> RGB
ContrastEnhancementFilter
|
Parameters: CLAHEClipLimit:2.0 |
|
Output: |
Contrast enhancement by CLAHE algorithm.
This filter enhance local contrast of image using algorithm CLAHE.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ContrastEnhancementFilter> <CLAHEClipLimit>2.0</CLAHEClipLimit>
</ContrastEnhancementFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
CLAHEClipLimit |
Parameter of local contrast enhancement procedure |
2.0 |
DilateFilter
|
Parameters: IterationCount:3 |
|
Output: |
Morphology operation 'Dilate'.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<DilateFilter> <IterationCount>1</IterationCount>
</DilateFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
IterationCount |
Number of iteration of procedure |
1 |
ErodeFilter
|
Parameters: IterationCount:1 |
|
Output: |
Morphology operation 'Erode'.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ErodeFilter> <IterationCount>1</IterationCount>
</ErodeFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
IterationCount |
Number of iteration of procedure |
1 |
GuoHallThinningFilter
Interface for thinning a binary image using Guo-Hall algorithm.
In details this algorithm is described in Kumar, H. and Kaur, P., 2011. A comparative study of iterative thinning algorithms for BMP images. International journal of computer Science and information Technologies (IJCSIT).
This filter has no parameters.
HistogramEqualizationFilter
This filter normalizes the image brightness and contrast by normalizing its histogram.
This filter have no parameters.
InvertFilter
|
Example |
Parameters: |
|
Input: |
Output: |
|
|
|
Interface for image color inversion.
This filter has no parameters.
OpenFilter
|
Example |
Parameters: |
|
Input: (zoomed in) |
Output: (zoomed in) |
|
|
|
Morphology operation 'Open'.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<OpenFilter> <IterationCount>1</IterationCount>
</OpenFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
IterationCount |
Number of iteration of procedure |
1 |
ZhangSuenThinningFilter
|
Example |
Parameters: |
|
Input: |
Output: |
|
|
|
Interface for thinning a binary image using Zhang-Suen algorithm.
In details this algorithm is described in Kumar, H. and Kaur, P., 2011. A comparative study of iterative thinning algorithms for BMP images. International journal of computer Science and information Technologies (IJCSIT).
This filter has no parameters.
ColorRangeConverter
Converts the color range of the image.
This filter creates the new image using the equation:
dst(x,y) = src(x,y) * Multiplier + Shift
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ColorRangeConverter> <Multiplier>1.0</Multiplier> <Shift>0.0</Shift>
</ColorRangeConverter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
Multiplier |
Multiplier (see eq.) |
1.0 |
|
Shift |
Shift (see eq.) |
0.0 |
BalanceWhiteFilter
Filter for white balance correction.
Equation that describes the output image:
dst(x,y) = WhiteBalance(src(x,y)) * Multiplier + Shift
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<BalanceWhiteFilter> <SaturationThreshold>0.9</SaturationThreshold> <Multiplier>1.8</Multiplier> <Shift>0.0</Shift>
</BalanceWhiteFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
SaturationThreshold |
Saturation threshold |
0.9 |
|
Multiplier |
Multiplier (see eq.) |
1.8 |
|
Shift |
Shift (see eq.) |
0.0 |
ColorBalanceFilter
Filter for color balance correction.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<BalanceWhiteFilter> <ColorBalanceGamma>1.0</ColorBalanceGamma> <SaturationGamma>1.0</SaturationGamma>
</BalanceWhiteFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
ColorBalanceGamma |
Color balance, less than 1 for warm colors, greater than 1 for cold colors. Range (0, 2). Limits are excluded. |
1.0 |
|
SaturationGamma |
Saturation coefficient. Range (0, 2). Limits are excluded. |
1.0 |
ColorSwapFilter
Filter for color channels swap.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ColorSwapFilter> <SwapPercent>1</SwapPercent> <SwappedChannels>RB</SwappedChannels>
</ColorSwapFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
SwapPercent |
Percent of swapping. Range [1 .. 100] |
1 |
|
SwappedChannels |
Swapped channels brief names. For example, “RB” for R <-> B channel swapping. |
RB |
6.4. Noise filters
BilateralFilterHuangBilateralFilter
MedianBlurFilter
BilateralFilter
|
Parameters: KernelSize:15|ColorSigma:170|SpaceSigma:210 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of generic bilateral filter.
This filter is described in Zhang, M., 2009. Bilateral filter in image processing.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<BilateralFilter> <KernelSize>5</KernelSize> <ColorSigma>100</ColorSigma> <SpaceSigma>150</SpaceSigma> </BilateralFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
KernelSize |
Size of kernel of bilateral filter |
5 |
|
ColorSigma |
Sigma for intensity range |
100 |
|
SpaceSigma |
Sigma for space range |
150 |
HuangBilateralFilter
|
Parameters: KernelSize:15|ColorSigma:170|SpaceSigma:210 |
|
Output: |
Implementation of Huang bilateral filter.
This filter is described in Huang, Y.L. and Fuh, C.S., 2006. Noise reduction using enhanced bilateral filter. Images and Recognition, 12(4), pp.46-53.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<HuangBilateralFilter> <KernelSize>5</KernelSize> <ColorSigma>100</ColorSigma> <SpaceSigma>150</SpaceSigma> </HuangBilateralFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
KernelSize |
Size of kernel of bilateral filter |
5 |
|
ColorSigma |
Sigma for intensity range |
100 |
|
SpaceSigma |
Sigma for space range |
150 |
MedianBlurFilter
|
Parameters: KernelSize:5 |
|
Output: |
Interface for median blur filter.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<MedianBlurFilter>
<KernelSize>5</KernelSize>
</MedianBlurFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
KernelSize |
Size of kernel of bilateral filter |
5 |
6.5. Special filters
CompositeFilterExternalFilter
CompositeFilter
Special filter for algorithms execution.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <CompositeFilter>
<AlgorithmsSetFilename>../AlgorithmsSet_sample.xml</AlgorithmsSetFilename> <AlgorithmName>SimpleAlgorithm</AlgorithmName> </CompositeFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
AlgorithmsSetFilename |
Name of file with algorithms description |
|
|
AlgorithmName |
Name of algorithm from selected set |
|
ExternalFilter
Filter for plugin usage.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
... <ExternalFilter> <PluginFileName>IPL_Plugin_sample.dll</PluginFileName> <PluginParametersString>1</PluginParametersString> </ExternalFilter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
PluginFileName |
Implementation of plugin with interface described in IPL_Plugin_Interface.h |
|
|
PluginParametersString |
String containing parameters plugin work. Format of this string is defined by concrete plugin developer |
|
7. Image information
InfoGetBoundariesInfoGetExif
InfoGetBoundaries
This operation allows detection of boundaries of the main object in the image. Please find further information in CIB aiModule.
Parameters of this function:
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
InfoGetBoundaries/Algorithm |
Which algorithm to use for border detection: New, Original, OriginalReduced, Ai. Ai requires the Ai module. |
New |
|
InfoGetBoundaries/ModelFilename |
Filename of the model for the Ai based algorithm |
- |
|
InfoGetBoundaries/ConfidenceIncluded |
Set “0” for correct boundary detection |
|
Output properties: Boundaries, and Edges.
Boundaries: 8 numbers separated with semicolons (’;’) that all together represent the 4 corners of the bounding box.
Edges: Each edge consist of 4 numbers split with semicolons (‘;’). These numbers represent a line defined from border to border of the image in the format X0;Y0;X1;Y1.
Example
<job> <steps> <step command="ipl"> <properties> <property name="OperationName">InfoGetBoundaries</property> <property name="Profile:InfoGetBoundaries/Algorithm">Ai</property> <property name="Profile:InfoGetBoundaries/ModelFilename">document_v1.pb</property> <property name="InputFilename">D:\PixelOne.jpg</property> <property mode="out" name="InfoGetBoundaries/Boundaries"/> <property mode="out" name="InfoGetBoundaries/Edges"/> </properties> </step> </steps>
</job>
Example (edges)
Request:
<property name="OperationName">InfoGetBoundaries</property>
…
<property mode="out" name="Profile:InfoGetBoundaries/Edges"/>
Output:
<property name="InfoGetBoundaries/Edges">
2550;0;2832;4048;2407;0;3048;4048;2263;0;3124;4048;2108;0;3191;4048;…
</property>
InfoGetExif
This operations extracts the Exif information from the input image.
There are no input parameters.
Output property: Exif.
8. Mergers
ImageChannelsMergerColorQRMerger
AlphaChannelMerger
ImageChannelsMerger
Merger for joining individual images.
Parameters of this merger can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ImageChannelsMerger> <TargetColorSpace>RGB</TargetColorSpace>
</RDO_Segmenter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
TargetColorSpace |
Target color space: RGB/GRAY |
RGB |
ColorQRMerger
Merger for joining individual images belonging to QR codes (experimental). Each input image represents a channel in the RGB color space.
There are no parameters for this merger, besides the images themselves. Maximum number of input images is limited to the range [1-3].
AlphaChannelMerger
Interface for tools for alpha channel merging.
Parameters of this merger can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<AlphaChannelMerger> <AlphaChannelValue>255</AlphaChannelValue>
</AlphaChannelMerger>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
AlphaChannelValue |
Value for alpha channel |
255 |
9. Segmenters
RangesSegmenterRDO_Segmenter
ColorQRSegmenter
SplitChannelsSegmenter
RangesSegmenter
Interface of image segmentation by color ranges.
This segmenter allows to extract from image to separated images all pixels with colors that fall within user defined ranges (or if it is required pixel that do not fall within these ranges). These ranges can be set by definition of lower and upper range boundaries:
<RangesSegmenter GetMasks="0"> <UsedColorSpace>RGB</UsedColorSpace> <LowerBoundaries>0,0,0;130,55,80;219,200,130</LowerBoundaries> <UpperBoundaries>128,128,128;209,190,190;255,255,191</UpperBoundaries>
</RangesSegmenter>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
UsedColorSpace |
Colorspace of an image |
RGB |
|
LowerBoundaries |
Lower boundaries of a range |
0,0,0;127,127,127 |
|
UpperBoundaries |
Upper boundaries of a range |
128,128,128;255,255,255 |
|
GetMasks |
Flag for masks |
0 |
RDO_Segmenter
Segmenter for extracting layers from an image.
This segmentation procedure is based on article Cheng, H. and Bouman, C.A., 2001. Document compression using rate-distortion optimized segmentation. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 10(2), pp.460-475. But RDO_Segmenter is modification of algorithm from the article.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<RDO_Segmenter> <ImageBlockSize>8</ImageBlockSize> <IsTextBinaryMaskRequired>true</IsTextBinaryMaskRequired> <ThreshHigh>150.0</ThreshHigh> <ThreshLow>25.0</ThreshLow> <ThreshMean>200.0</ThreshMean> <DCTCoeff>400</DCTCoeff> <ThreshVariance>25</ThreshVariance> <IsDownsamplingRequired>false</IsDownsamplingRequired> <RatioForeground>4.0</RatioForeground> <RatioBackground>2.0</RatioBackground>
</RDO_Segmenter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
ImageBlockSize |
Size of image blocks for processing |
8 |
|
IsTextBinaryMaskRequired |
Flag for result layers filling |
true |
|
ThreshHigh |
High threshold for the segmenter |
150.0 |
|
ThreshLow |
Low threshold for the segmenter |
25.0 |
|
ThreshMean |
Mean threshold for the segmenter |
200.0 |
|
DCTCoeff |
Threshold for discrete cosine transform |
400 |
|
ThreshVariance |
Variance threshold |
25 |
|
IsDownsamplingRequired |
Flag for optional background and foreground downsampling |
false |
|
RatioForeground |
Scale factor for foreground downsampling |
4.0 |
|
RatioBackground |
Scale factor for background downsampling |
2.0 |
ColorQRSegmenter
Segmenter for extracting layers from a QR RGB image (experimental). It only accepts 1 input image, and outputs 3 images, one per channel.
Parameters of this filter can be described in profile:
<ProcessingProfile>
...
<ColorQRSegmenter> <IsTextBinaryMaskRequired>true</IsTextBinaryMaskRequired>
</ColorQRSegmenter>
...
</ProcessingProfile>
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
MaxSide |
Longest side for rescaling |
0 |
|
CleanBackground |
If enabled it attempts to clean the background |
false |
|
Blur |
If enabled it will execute blurring |
false |
|
Sharp |
If enabled it will add a sharp filter |
false |
|
HueDiscretization |
If enabled it will use HUE discretization to process the image |
false |
|
Grayscale |
If enabled, final image will not be binarized |
false |
SplitChannelsSegmenter
This segmenter allows to separate multichannel image to few grayscale images with one channel.
There are no parameters for this segmenter.
10. Image comparer
ComparePSNR
Compares two images and return the PSNR.
Output property: PSNR.
CompareDifference
Compares two images and return the difference.
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
ScaleX |
Value to scale X axis. |
-1.0 |
|
ScaleY |
Value to scale Y axis. |
-1.0 |
|
nProcessedImageSize |
Use this to scale the image (long side). Only if ScaleX and ScaleY are less than 0. |
512 |
Output property: Difference.
11. Algorithms sets
Algorithms sets are used for describing of complex image processing procedures. Algorithm can be described in two ways:
- sequence of image filters,
- directed graph of image processors.
<algorithms> ...
<algorithm name="SimpleAlgorithm">
<filter type="HuangBilateralFilter" params="KernelSize:11" />
<filter type="SavoulaBinarizerFilter" params="WindowSize:101|ThresholdCoefficient:0.015" />
<filter type="OpenFilter" params="IterationCount:2" />
</algorithm> ...
</algorithms>
This sample shows sequential filtration of single input image by three filters:
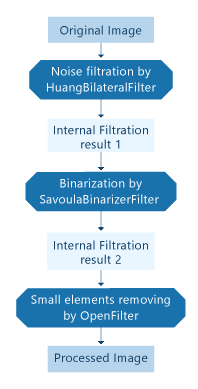
The second way allows usage of all processors (filters, segmenters, mergers). In this case we describe algorithm as set of processor blocks combined to layers and input/output of each block. For example:
<algorithms>
...>
<algorithm name="GraphAlgorithm" inputs="in1=$1|in2=$2" outputs="l1p1o1=$1|l2p1o1=$2">
<layer>
<processor type="ColorRangesFilter" params="IsMaskOnlyRequired:0|IsInRangeColorsRequired:1|LowerBondaries:0,0,0|
UpperBondaries:96,96,96"
inputs="in1" outputs="l1p1o1" />
<processortype="ColorSpaceConvertionFilter" params="TargetColorspace:GRAY" inputs="in2" outputs="l1p2o1" />
</layer>>
<layer>
<processor type="AlphaChannelMerger" params="AlphaChannelValue:128" inputs="l1p1o1|l1p2o1" outputs="l2p1o1" />
</layer>
</algorithm>
...
</algorithms>
This sample shows processing of two files with further merging of preliminary processing results:
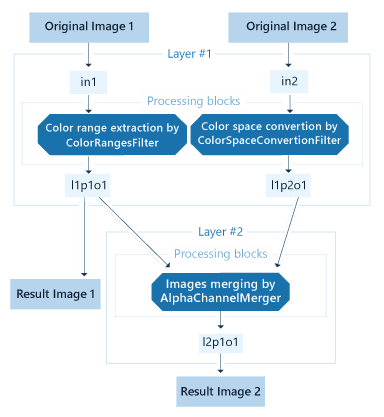
12. CIB aiModule
DescriptionProperties
Description
Currently, CIB aiModule is only called via CIB image toolbox. Its functionality is to detect boundaries in order to auto crop images correctly.
The following libraries are required to run CIB aiModule:
|
Version |
Library |
|
Windows 64 |
CibAiModule64.dll, tensorflow.dll |
|
Linux x86 64 |
libcibaimodule64.so, libgcc_s.so.1, libstdc++.so.6, libtensorflow.so, libtensorflow_framwork.so |
|
Android x86 64 |
libcibaimodule64.so |
|
Android arm 64 |
libcibaimodule64.so |
Properties
The following properties are required for CIB image toolbox to call cropping with CIB aiModule:
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
OperationName |
Name |
InfoGetBoundaries |
|
Profile:InfoGetBoundaries/Algorithm |
Which algorithm to use for border detection: New, Original, OriginalReduced, Ai. Ai requires the Ai module. |
Ai |
|
Profile:InfoGetBoundaries/ModelFilename |
Path to the file that contains trained data for requested operation (now only image-cropping model exists) |
<Path_To_Model_File> |
|
Profile:InfoGetBoundaries/ConfidenceIncluded |
|
0 |
Further supported input properties of CIB aiModule:
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
InputMemoryAddress |
string representation of an address in the memory where input image data is provided (image data as an in-memory Bitmap) |
- |
|
Width |
Width of the input image, provided by InputMemoryAddress |
- |
|
Height |
Height of the input image, provided by InputMemoryAddress |
- |
Output properties of CIB aiModule:
|
Property name |
Description |
Default value |
|
Result |
Contains the result. For image-cropping, the result contains XY-coordinates of four vertices (8 numbers) in string format, numbers are separated by semicolon |
- |
13. Returncodes
|
Returncode |
Meaning |
|
2101 |
Memory could not be allocated |
|
2102 |
Input job handle is not set or incorrect |
|
2103 |
Input Parameter has not been set |
|
2104 |
Output parameter is not set or incorrect |
|
2105 |
Invalid Property Name (Preview Creation/ Image Processor) |
|
2106 |
Required Property is not defined |
|
2108 |
Property Value could not be set |
|
2109 |
Property Value could not be read |
|
2110 |
empty or invalid parameter (e.g. input/output directory or file) |
|
2111 |
Error while reading file |
|
2112 |
Error while parsing image to cv.MAT format |
|
2113 |
Both, input file AND blob, are defined |
|
2120 |
Runtime error |
|
2130 |
Initialization error |
*This table contains errors of the IPL. Bold errorcodes indicate standard returncodes.